Extending the Map
Map view displays cluster resource on a graph. Plugins can extend this graph by adding nodes and edges.
Nodes, edges and sources
Node represents a Kubernetes resource. Edges connect different nodes, for example ReplicaSet connects to Pods it owns.
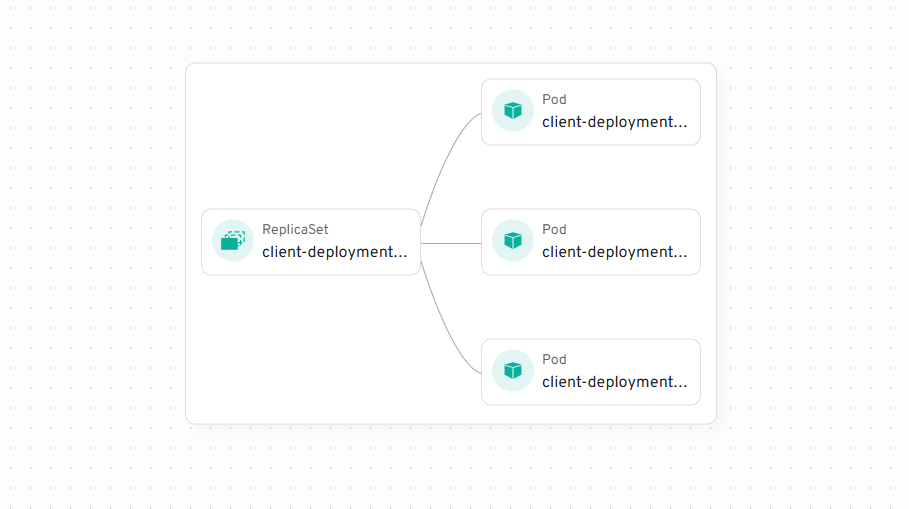
To add your own nodes and edges you need to define a Source
A graph Source represents a collection of Nodes and Edges along with name and icon. Source may contain other Sources.
Creating and registering a Source
To define a Source create an object with the following structure:
const mySource = {
id: "my-source", // ID of the source should be unique
label: "My Source", // label will be displayed in source picker
// you can provide an icon
icon: (
<img
src="https://headlamp.dev/img/favicon.png"
alt="My Source logo"
style={{ width: "100%", height: "100%" }}
/>
),
/**
* useData is a hook that will be called to load nodes and edges for your source
* You can use hooks here that Headlamp provides to load Kubernetes resources
* this hook should return an object with nodes and edges or `null` if it's loading
* it's important that return object is not recreated every time, so useMemo is required
*/
useData() {
return useMemo(() => {
// This would come from kubernetes API but it's hardcoded here as an example
const myResource = {
kind: "MyResourceKind",
metadata: {
uid: "1234",
name: "my-test-resource",
namespace: "test-namespace",
creationTimestamp: "1234",
},
};
const edges = []; // no edges in this source
const nodes = [
{
id: myResource.metadata.uid, // ID should be unique
kubeObject: new KubeObject(myResource),
// Optionally provide a custom details component to be shown when node is selected
detailsComponent: ({ node }) => {
return (
<div>
<h2>Custom Details View</h2>
<p>
This is a custom details view for:
{node.kubeObject.metadata.name}
</p>
</div>
);
},
},
];
return { edges, nodes };
}, []);
},
};
Then to register it call registerMapSource
registerMapSource(mySource);
You'll now see it in the Source picker and the Node on the Map:


Node Icons
To add an icon to the Node you need to call registerKindIcon.
Note: This is different from the Source icon. One Source may contain multiple different kinds of objects.
registerKindIcon("MyCustomResource", {
// icon is a JSX element
icon: <img src="https://headlamp.dev/img/favicon.png" />,
});

Custom Detail Views
When a node is selected on the map, its details are shown in a side panel. By default, if the node represents a Kubernetes resource (has kubeObject property), Headlamp will show the standard resource details view.
You can override this behavior by providing a custom details component:
const myNode = {
id: "custom-node",
label: "Node with custom details",
detailsComponent: ({ node }) => {
return (
<div>
<h2>Custom Details</h2>
<p>This is a custom details view for: {node.label}</p>
{/* You can access any node property here */}
<pre>{JSON.stringify(node, null, 2)}</pre>
</div>
);
},
};
The details component receives the node object as a prop, giving you access to all node properties.
This is useful when you want to:
- Show custom visualizations for your resources
- Display data from external sources alongside Kubernetes resources
- Create interactive detail views specific to your use case
Custom Glance Component
When hovering over a node in the map, a preview (or "glance") is displayed. For Kubernetes resources, Headlamp provides default glance components. You can register a custom glance component for any node type (Kubernetes or custom) using registerKubeObjectGlance.
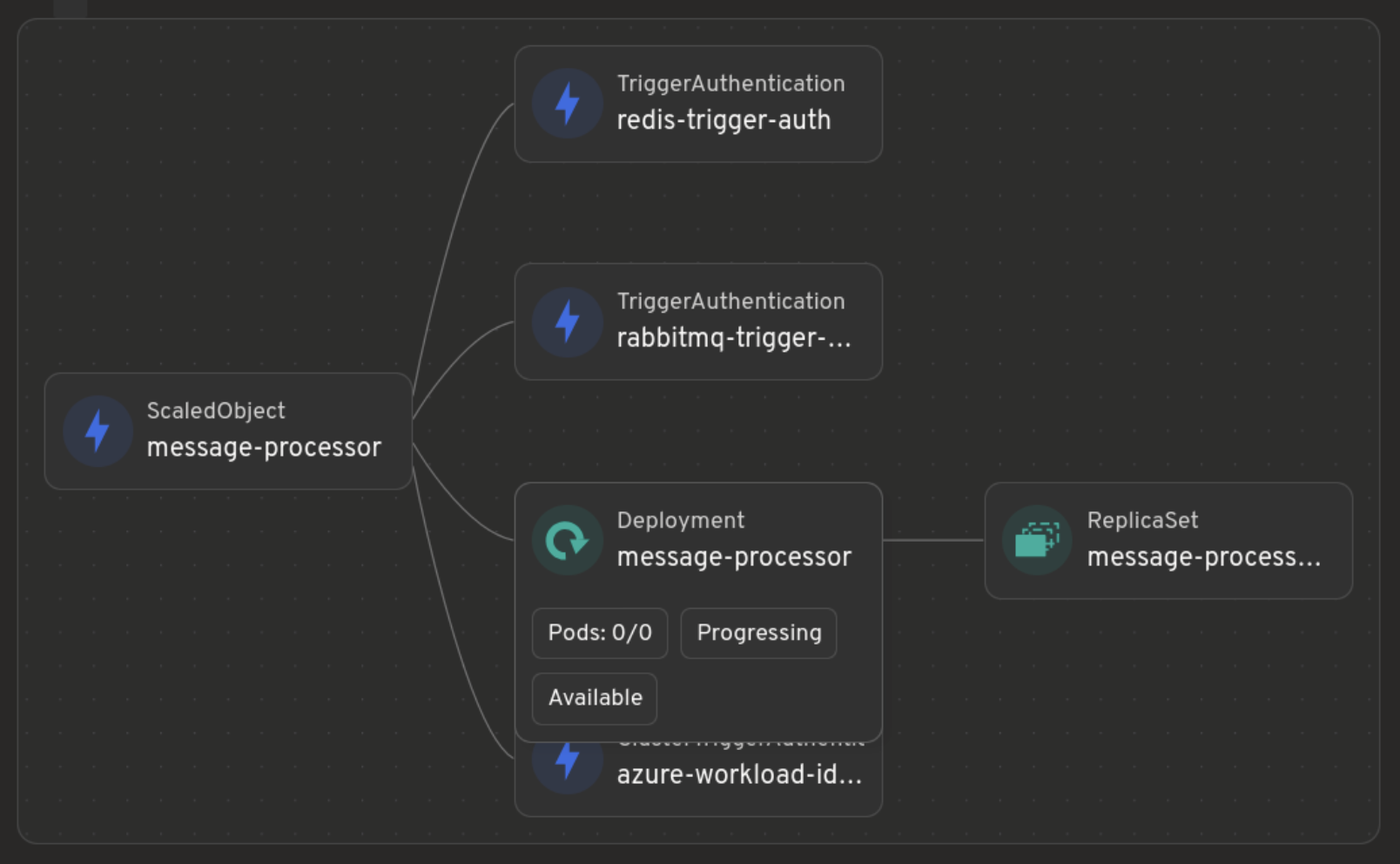
Here's how you can register a custom glance component:
const CustomNodeGlance = ({ node }) => {
// Check if the node represents a Kubernetes object
if (node.kubeObject) {
return (
<div>
<strong>{node.kubeObject.kind}:</strong>{" "}
{node.kubeObject.metadata?.name}
</div>
);
}
// Handle non-Kubernetes nodes with label or fallback to a default
if (node.label) {
return (
<div>
<strong>Node:</strong> {node.label}
</div>
);
}
// Return null if the node cannot be rendered by this glance
return null;
};
registerKubeObjectGlance({ id: "custom-node", component: CustomNodeGlance });